asadmin is a command-line tool for GlassFish , which provides a series of subcommands. Using asadmin, you can complete all management tasks of GlassFish.
The subcommand start-domain of asadmin can start GlassFish. The following will describe the main process of GlassFish startup, starting from the execution of the asadmin command.
# asadmin Execution Process
The entry point of the asadmin command is org.glassfish.admin.cli.AsadminMain, which is included in the ${AS_INSTALL_LIB}/client/appserver-cli.jar package.
The main process of AsadminMain execution is as follows:
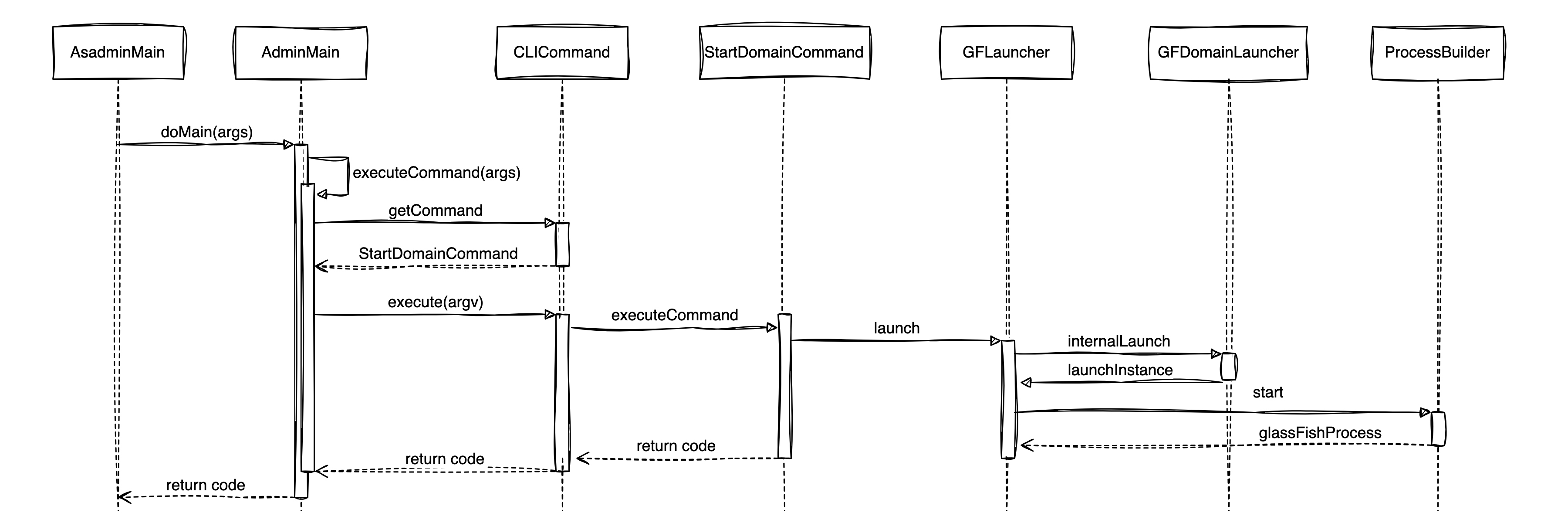
Some key points:
-
The
CLICommand.getCommand()is called to obtain the subcommand to start the GlassFish. All subcommands ofasadmininherit from com.sun.enterprise.admin.cli.CLICommand and are loaded from the following directories or Jars:-
${com.sun.aas.installRoot}/lib/asadmin
-
${com.sun.aas.installRoot}/modules/admin-cli.jar
-
-
All subcommands are executed by calling
CLICommand.execute(String... argv). -
The implementation class of the subcommand to start
GlassFishis StartDomainCommand, which internally callsGFLauncher.launch()to start theGlassFish. -
Finally, GFLauncher uses ProcessBuilder to start a new process, which is the main process of
GlassFish. The entry point of this new process is com.sun.enterprise.glassfish.bootstrap.ASMain.
In addition, if the verbose or watchdog is set, the parent process asadmin will not exit and will wait until GlassFish runs to the end:
|
|
Next, we analyze the startup process of the GlassFish main process.
# Main Process Startup Process
The entry point of the GlassFish main process is the main method of com.sun.enterprise.glassfish.bootstrap.ASMain , and the main process of the startup process is as follows:
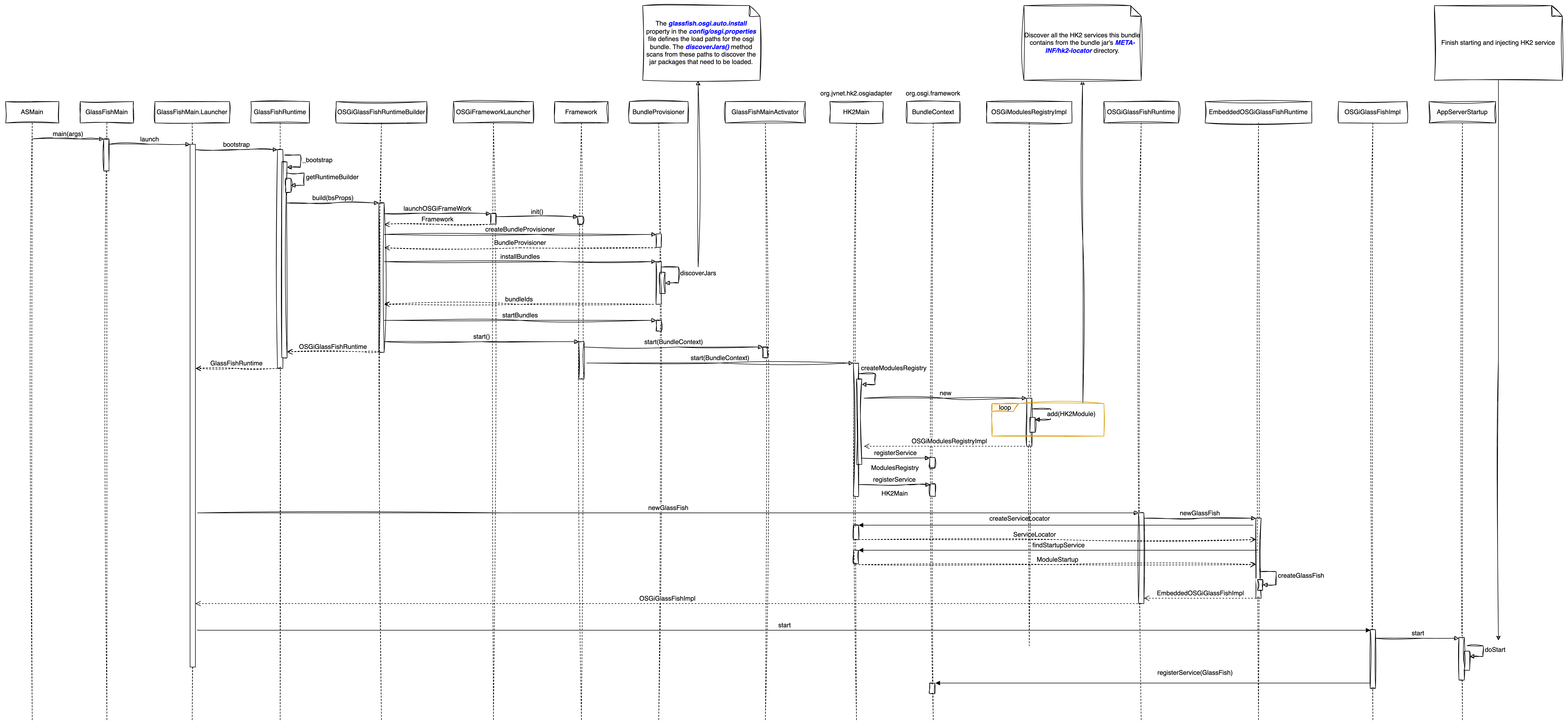
The startup process is complicated, but the main steps are clear:
- Create GlassFishRuntime using RuntimeBuilder
- Create a GlassFish instance using GlassFishRuntime
- Start the
Glassfishinstance by callingGlassFish.start()
# Creating GlassFishRuntime
The main steps to create GlassFishRuntime include:
- Create RuntimeBuilder
- Create and initialize the OSGi Framework
- Load OSGi bundles
- Start the OSGi Framework
- Start the BundleActivator in the bundles
- During the startup process of HK2Main, it searches for and registers HK2 modules.
During the creation of GlassFishRuntime, OSGiGlassFishRuntimeBuilder will create and initialize the OSGi Framework, and then use the installBundles() method of BundleProvisioner to install all bundles of GlassFish to OSGi.
Where does BundleProvisioner find the bundles to load? The glassfish.osgi.auto.install property in the ${com.sun.aas.installRoot}/config/osgi.properties file defines the loading path of OSGi bundles. The discoverJars() method of BundleProvisioner will scan these paths and discover the Jar packages that need to be loaded.
After completing the loading of bundles, OSGiGlassFishRuntimeBuilder will call Framework.start() to start the OSGi Framework. During the startup process of the OSGi Framework, the BundleActivator in the bundles will be started. Two important BundleActivators are:
During the startup process of GlassFishMainActivator , EmbeddedOSGiGlassFishRuntime will be registered in OSGi.
HK2Main will create ModulesRegistry. ModulesRegistry is a key component of HK2. All modules in HK2 are registered here. In the OSGi environment, the specific implementation class of ModulesRegistry is OSGiModulesRegistryImpl, which will find and register the HK2 modules contained in the META-INF/hk2-locator directory of all bundle Jars.
ModulesRegistry and HK2Main will be registered as OSGi’s service.
# Creating GlassFish Instance
Create a GlassFish instance through GlassFishRuntime.newGlassFish(). This process mainly does two things:
- Create HK2’s ServiceLocator
- Get ModuleStartup from ServiceLocator
In EmbeddedOSGiGlassFishRuntime, use ModulesRegistry.newServiceLocator() to create ServiceLocator, and then get ModuleStartup from ServiceLocator. In the GlassFish startup scenario, the specific implementation of ModuleStartup is AppServerStartup.
ServiceLocator is the registry of HK2 services, which provides a series of methods to get HK2 service.
The relationship between HK2 Module and Service can be regarded as the relationship between container and content. Module (container) contains a group of Service (content) and is responsible for registering these Services in ServiceLocator. When a Module is initialized, all its Services will be registered in ServiceLocator, and then these Services can be found and used by other Services.
Finally, create a GlassFish instance with AppServerStartup and ServiceLocator as the parameters of the constructor.
# Starting GlassFish Instance
Use GlassFish.start() to start the Glassfish instance. The most critical step is to call AppServerStartup.start(), which starts the HK2 service in stages. The service of HK2 can specify the startup level, the lower the level, the earlier the startup.
After AppServerStartup.start() runs, all services start, and Glassfish completes startup and runs.